Home / Compare Electricity & Ga… / Solar batteries: What yo…
Solar batteries: What you should know
Compare solar feed-in tariffs with Compare the Market






Key takeaways
- If you have rooftop solar panels, you may want to invest in a solar battery to store your solar power for when the sun isn’t shining.
- There are several different types of solar batteries that you can choose from when getting a solar battery installed.
- Before deciding to install a solar battery, you may want to consider the potential costs involved plus how a solar battery could benefit you.
Expert tips on managing your electricity with solar
Our Head of Energy, Meredith O’Brien, has some top tips to help you understand your solar photovoltaic (PV) system and your energy plan.

Consider what size battery you need
When looking for the right battery size for your solar PV system, check what size battery may be appropriate; consider your average daily usage of electricity and the amount of solar energy generated from your solar panels. If you have a sizeable solar system, you may need multiple batteries.
You’ll still receive an electricity bill
Having solar batteries doesn’t necessarily mean you’re off-grid, and in most cases, you’ll still need a connection to the grid. This means even if your solar panel system covered all your electricity usage costs, you would still receive a bill for the cost of supplying electricity to your property.
Compare and save
While a solar system and solar battery can help lower your electricity bills, that doesn’t mean you can’t search for more savings by comparing. You can compare electricity plans across a range of providers. Y can also compare solar feed-in tariffs and potentially save by sending your excess solar power back to the grid. Consider looking for new plans on offer with the introduction of two-way solar charging. This may offer great solar feed-in tariff offers to export during period periods that rely on stored battery power (i.e. at night or when the sun isn’t shining).
Understand solar batteries and how they work
What is solar battery storage?
Solar energy storage systems work on the same principle as other rechargeable batteries. Essentially, they give you an easy way to store electricity, which you can use later as required. This gives you a reliable cache of solar-generated power to fall back on during the night or on dark and cloudy days.
What are the different types of solar batteries?
There are a few different types of energy storage batteries that may be appropriate for your solar system, depending on your budget and energy needs:
- Lead-acid batteries. One of the older and more common types of solar batteries, lead-acid batteries are cheaper than most on the market. However, they’re also slow to charge, require regular maintenance, are bulker than other batteries and don’t last as long.
- Lithium-ion batteries. In recent years, lithium-ion batteries have begun to overtake lead-acid batteries due to their longer lifespan and greater storage capacity in comparison to their size. While more expensive than lead-acid batteries, they’ve dropped in price in recent years. However, they can be a potential fire hazard if inadequately installed.
- Liquid ‘flow’ batteries. Flow and flywheel batteries use liquids to store energy. They’re easily maintained, fire resistant and the longest-lasting type of solar battery, but they’re the most expensive and don’t generally store as much energy as lithium-ion batteries.1
How do solar batteries work?
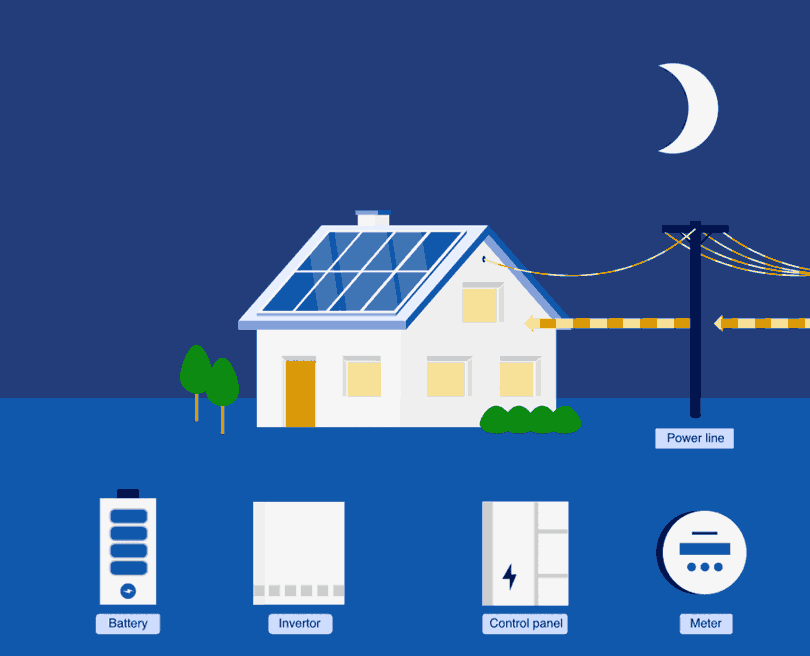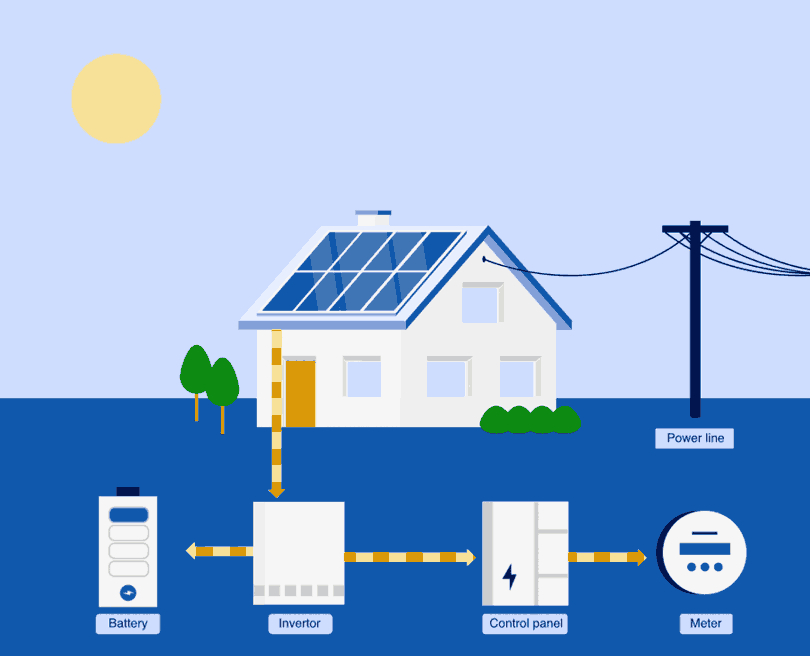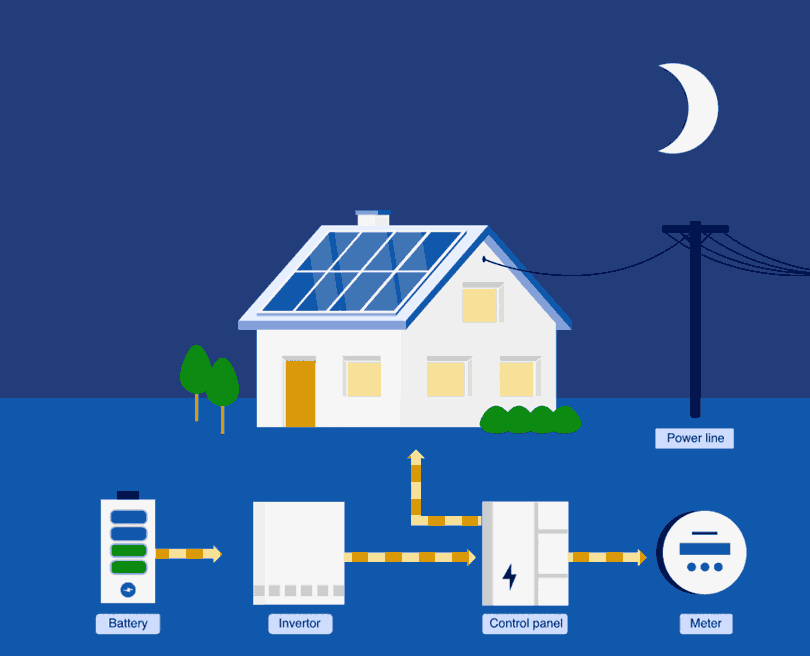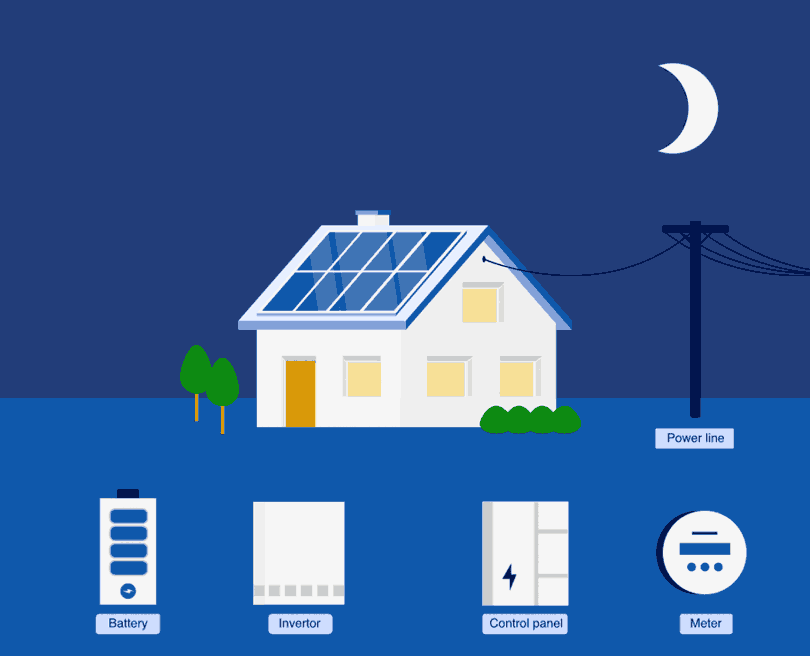 Most home solar battery systems need an inverter that turns the raw power generated from the solar panels (a direct current) into electricity that can be used by your home (an alternating current).2 The inverter then directs any unused excess energy into your batteries during the day.
Most home solar battery systems need an inverter that turns the raw power generated from the solar panels (a direct current) into electricity that can be used by your home (an alternating current).2 The inverter then directs any unused excess energy into your batteries during the day.
When the sun goes down and the solar panels stop producing power, your inverter will ‘turn around’ and energy can be drawn from your solar batteries to power your appliances as you need it. Inverters typically only need to be replaced every 10 to 15 years.1
Depending on your solar system and batteries, you might be able to adjust your settings in real time to control a few things. For example, you might want to change:
- Where the generated solar energy is sent (either to your home battery storage or to the local grid).
- Solar energy usage from your batteries during the day – it can be useful to set a cap on your daytime solar energy usage to ensure you have enough to last through the night.
Once your batteries are fully charged, you can send excess power to the grid. Your inverter will flip to sending additional power to the local grid until you adjust the settings and draw on your own battery power. Otherwise, this excess power could be ‘lost’.
What are the benefits of investing in a battery storage system?
A solar battery storage system can be a big investment, so it’s important to weigh up the benefits to decide if it’s right for you. Some of the main pros of getting a solar battery include:
- Harness more solar energy. By storing solar energy, you can harness even more solar power from the sun through your solar PV system. This means you have greater energy independence and need less electricity from the energy grid, which can help you reduce your energy bills.
- Off-grid systems can work during blackouts. If your solar battery inverter is off-grid, you can potentially use the backup power stored in your battery during a blackout or other power outage.
- Take advantage of solar feed-in tariffs. Homeowners and businesses can still receive credits on their electricity bill even with a solar battery by sending excess solar power back to the grid. Solar feed-in tariffs are the rate credited to you by your retailer for the electricity you generate from your solar panels and feed to the grid. Additionally, once the two-way charge (known as the sun tax) comes into effect 1 July 2025, a battery may help you avoid export charges during the day and attract better solar feed-in tariffs during the evenings.
- Lower your environmental impact. Solar energy is a growing source of renewable energy that helps reduce Australia’s carbon footprint. It’s a form of clean energy that allows us to move away from those sources that release large amount of greenhouse gas emissions, such as fossil fuels.
- Option to join a Virtual Power Plant. If you have a solar battery, you may be eligible to join a Virtual Power Plant (VPP) and join a network of connected solar batteries. This means your battery may be drawn on by the VPP during peak demand times to help stabilise the grid. By joining a VPP, you might receive incentives such as a discount on your electricity bills.
Are solar batteries worth it?
Whether solar batteries are worth it will depend on your individual circumstances, your budget, the size of your system and how much electricity your household uses. However, in general, solar storage batteries can help you get more out of your solar panels and lower your electricity bills.
In Australia, a home solar system can pay itself off in seven to nine years, or even as quickly as three to five years if you receive a solar rebate from your state or territory government to help reduce costs.3 However, your payback period will increase if you also purchase a solar battery.
Getting a solar battery for my home
How much do solar batteries cost?
 The cost of solar battery systems and battery installation for Australian households and small businesses will vary based on the type of battery and its size, though on average, solar batteries may cost $1,500 per kilowatt hour (kWh) of electricity you want from them.4 For example, a mid-sized battery may be around 10kW, meaning you could expect to pay around $15,000 (without rebates).
The cost of solar battery systems and battery installation for Australian households and small businesses will vary based on the type of battery and its size, though on average, solar batteries may cost $1,500 per kilowatt hour (kWh) of electricity you want from them.4 For example, a mid-sized battery may be around 10kW, meaning you could expect to pay around $15,000 (without rebates).
Be sure to check for potential rebates on your solar power system in your state or territory or interest free loans to help reduce upfront costs.
How long do solar battery home systems last?
Solar batteries will last for different lengths of time, depending on factors such as what your climate is like, how often you use it and where it’s installed. While solar batteries do eventually die, proper maintenance and use can help prevent your system from needing a replacement battery before its expected life cycle ends.
For example, charging your battery too frequently can shorten its lifespan, so be sure to only charge it as needed and recommended.
What size solar battery do I need?
When deciding on the right solar battery size, it’s important to choose one that matches both the output of your solar panels and the amount of power your home uses, not necessarily just the biggest battery that you can get. Small homes or single person households may only require a small solar battery, while someone with a large family or who is looking to become less reliant on the electricity grid would require a larger battery capacity.
You should contact a professional solar installer to assess what system size and type of solar battery bank best suits your energy goals.
Do solar batteries have a warranty?
Most solar batteries for houses and businesses have a warranty, which can last for a few years, though it may differ between manufacturers. It’s important you understand what’s covered by your warranty and what you need to do so your solar inverter and battery last as long as possible.
Can I go off-grid by using a solar battery at home?
It’s possible, but difficult, to go completely off-grid with a solar battery system. You need to ensure that:
- You have the right size solar system
- Your solar panels generate enough power to meet your needs
- You have the relevant invert capability to store multiple batteries
- Your batteries can store enough power for periods without any sun (e.g. rainy days)
- You have a back-up source of power (e.g. a diesel fuelled generator).
Otherwise, you’ll likely still require a connection to the local energy grid so you can draw on electricity from it in case you run out of solar power from your batteries.
Meet our Head of Energy, Meredith O’Brien
As the Head of Energy at Compare the Market, Meredith O’Brien believes in educating Australian customers about the everchanging gas and electricity market so they can adjust their energy usage habits and get the most out of their energy plans.
Meredith has six years within the energy industry, following 15 years of experience in financial services and is currently studying a Master of Business Administration. Meredith is a dedicated customer advocate who is passionate about empowering Australians to find the right products to suit their needs by removing the confusion from comparing.
Want to know more about energy?
1 Department of Planning, Industry and Environment, Government of New South Wales. NSW Home Solar Battery Guide. Published 2020. Accessed January 2025.
2 Department of Planning, Industry and Environment, New South Wales Government. Solar PV and Batteries. Accessed January 2024.
3 Solar Victoria, Department of Environment, Water, Land and Planning, Australian Government. Solar Panel (PV) Buyers Guide – Section 1: Why install a solar electricity system at home? Last updated February 2023. Accessed January 2025.
4 Solar Victoria, Department of Environment, Water, Land and Planning, Australian Government. Is a solar battery right for your home? Accessed January 2025.