Natural gas is a source of energy that’s been used for more than 100 years in Australia, helping to power specific appliances in our homes as well as meeting the energy needs of large industries.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
Natural gas is a type of fossil fuel formed from decomposing plant and animal matter. This matter gets trapped underground, and over millions of years, pressure and heat from deep under the Earth’s crust turn this into a pocket of fossil fuel underground.
Commonly, natural gas is found close to oil deposits (which are turned into petrol) close to the surface, but more significant deposits are typically deeper down.1
Natural gas can also be produced and harnessed from landfills as well in a similar way to biofuel, which is a renewable energy source.
On its own, natural gas is colourless and odourless. As it’s also flammable, leaks can be dangerous and hard to detect without additional chemicals being added to it as a part of the refining process. For example, mercaptan is a chemical that’s added to give gas the distinct ‘rotten egg’ smell, making it easy to detect a leak.
Other types of gas fuels are manufactured through chemical reactions and not found underground, though they may share some common elements.

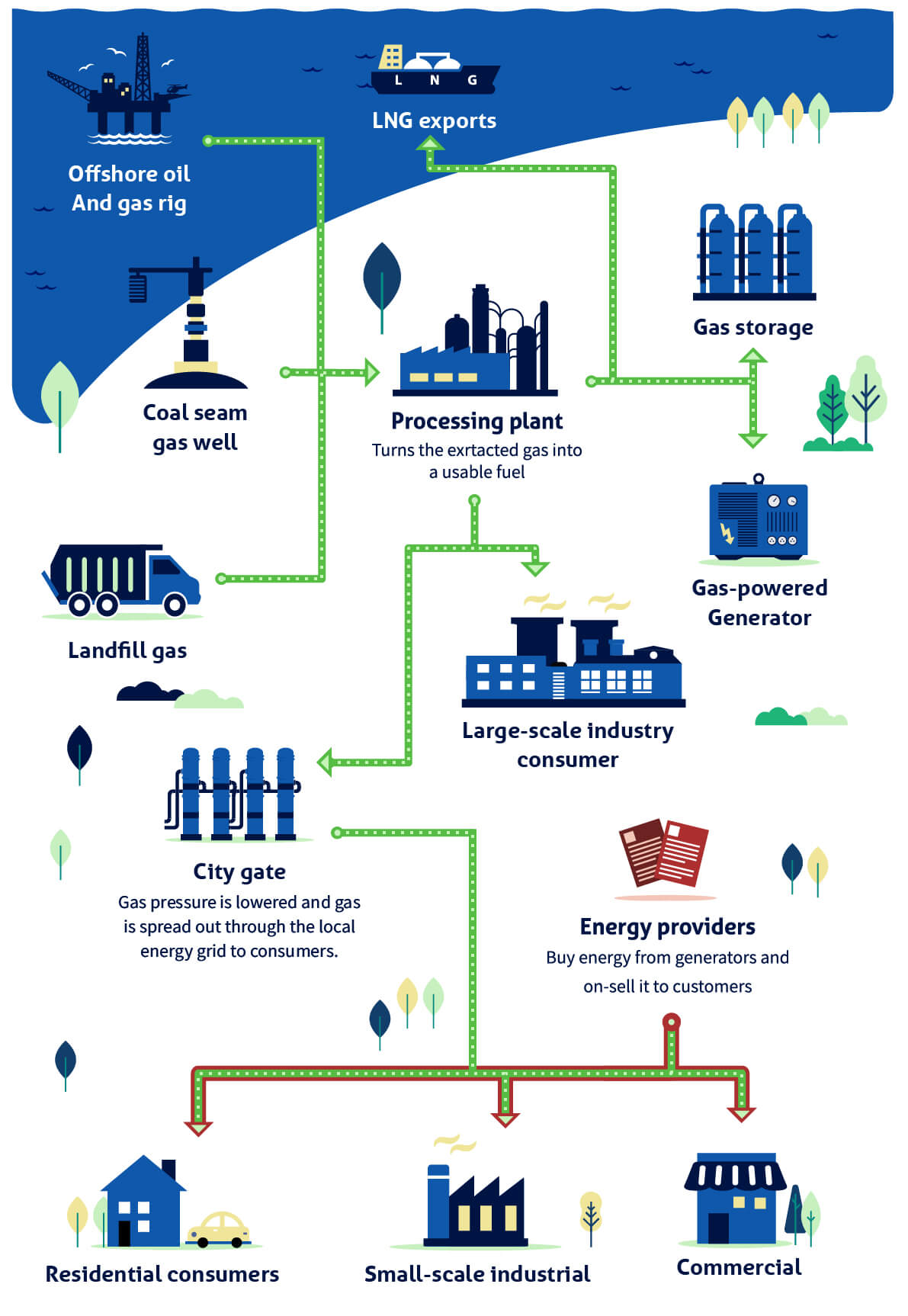
Large-scale extraction sites use drills to dig a hole down to the gas pocket. The natural gas can then be ‘sucked-up’ or harvested before being processed into fuel and then shipped to a network of pipes, known as gas mains, that form part of the energy grid.
The composition of elements and materials can lead to different natural gas chemical formulas. This gas is then processed to remove unwanted elements. Natural gas is mostly comprised of methane (before chemicals like mercaptan are added to it).2
Once refined into a fuel, gas is transported by a network distributor underground alongside other utilities like water. Your home can then be connected to a natural gas network if it’s available in your area.
Check out our guide to how natural gas goes from the gas well that extracts it to your home or business.
Only a few purpose-built devices and appliances at your home use gas. These can include:
Most of these have electric options as well, which are generally cheaper to install or buy, but cost more to run than their gas counterparts.
Learn more about the difference in costs between gas and electricity here.
Natural gas is used for heating and cooking, as well as in the production of electricity.
There are other uses for natural gas too. It can be turned into a liquid natural gas (LNG), which can be stored for later or exported across the world to other countries. It can be sent to a gas-powered power plant and burned to spin a turbine to create electricity, which is then fed back into the energy network.
Some large-scale industrial natural-gas consumers may be connected straight from the processing plant that turns the extracted gas into a usable fuel.
Technically, this natural gas can be considered both a renewable and non-renewable source of energy, depending on its source. If it’s harvested from gas pockets underground, it isn’t technically a renewable source of energy. However, natural gas can also be harvested from landfills, and this method of harvesting gas fuel is renewable.
Natural gas is a fossil fuel, made from decomposing matter and pressure underground. When it’s harvested and burned it provides energy, but it also gives off carbon dioxide emissions.
Producing and using natural gas does create carbon emissions, which are harmful to the environment. Gas emissions are lower than the emissions made by electricity generated from coal-fired power stations, making it the most environmentally friendly fossil fuel.3
Electricity usage is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), while gas usage is measured in megajoules (MJ), except in Western Australia where it is measured in Units (one Unit is equal to 3.6MJ). Your gas consumption is measured at your home’s gas meter, which looks a lot like electricity meters, but it records MJ consumption in cubic metres (M3). You can learn more about how to read your energy bills with our helpful explainer.
Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) can be made from harvesting natural gas or oil, meaning LPG can be considered a natural gas. Unlike gas mains that are connected underneath the house, LPG is bottled in a liquid form in metal, pressurised containers.
You’ll typically see LPG connected to BBQs, portable ovens, grills and fireplaces. Sometimes there will be a large LPG cylinder connected to the side of the home that’s connected to each gas appliance. You’ll need to get the container replaced or refilled when it runs out.
If you use gas appliances at home, you could potentially save money by comparing gas plans in your area. Our free comparison service is easy to use, only takes minutes, and helps you compare usage fees, supply charges and tariffs from a number of energy providers.
Simples!
1 Natural gas explained. U.S. energy Information Administration, Government of the United States of America. 2019.
2 Gas. Geoscience Australia, Australian Government. 2020.
3 Australian electricity options: natural gas. Ian Cronshaw, Crawford School, Australian National university, Parliament of Australia. 2020.